The merge process is a critical component of data management and integration, where data from multiple sources is combined to create a unified, comprehensive dataset. This process is essential for organizations that need to consolidate information from various systems, departments, or external sources to gain a holistic view of their operations, customer base, or market trends.
Understanding the Merge Process
The merge process involves the systematic integration of data from disparate sources into a single, cohesive dataset. This process typically includes steps such as data extraction, data cleansing, data transformation, and data reconciliation, all of which are designed to ensure the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of the final dataset.
Key Steps in the Merge Process
- Data Extraction: The first step in the merge process is to extract data from various sources, such as databases, spreadsheets, or external APIs.
- Data Cleansing: Once the data has been extracted, it needs to be cleaned and standardized to ensure consistency and accuracy. This may involve removing duplicates, fixing formatting issues, or addressing missing or invalid data.
- Data Transformation: The next step is to transform the data into a format that can be easily integrated with the target system or database. This may involve mapping fields, converting data types, or performing calculations.
- Data Reconciliation: The final step in the merge process is to reconcile the data from different sources, ensuring that any discrepancies or conflicts are resolved and that the final dataset is a true representation of the underlying information.
Common Challenges in the Merge Process
The merge process can be complex and challenging, with a variety of potential pitfalls that organizations must navigate. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Data Quality Issues: Inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate data can make it difficult to effectively merge datasets.
- Data Formatting Differences: Variations in data formats, such as date or time representations, can complicate the merge process.
- Duplicate Records: Identifying and removing duplicate records is a critical but often time-consuming task.
- Organizational Silos: Lack of communication or cooperation between different departments or teams can hinder the merge process.
Importance of Data Quality in the Merge Process
The quality of the data being merged is of paramount importance, as it directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the final dataset. Poor data quality can lead to erroneous insights, flawed decision-making, and even legal or regulatory issues. Ensuring high-quality data throughout the merge process is essential for the success of any data integration initiative.
Different Types of Data Merging
There are several different types of data merging, each with its own unique characteristics and requirements:
- Horizontal Merging: Combining data from multiple sources that have the same set of fields or attributes.
- Vertical Merging: Combining data from multiple sources that have the same set of records or entities.
- Fuzzy Merging: Combining data from multiple sources that have similar but not identical fields or records.
Examples of Successful Merge Processes
Many organizations have successfully implemented effective merge processes, leading to improved data quality, enhanced decision-making, and better overall business performance. Some notable examples include:
- Retail Chains: Merging data from multiple store locations, online sales, and customer loyalty programs to gain a comprehensive view of their customer base and buying patterns.
- Financial Institutions: Integrating data from various banking, investment, and insurance products to provide a holistic financial profile for their customers.
- Healthcare Organizations: Combining patient records from multiple clinics, hospitals, and laboratories to improve patient care and outcomes.
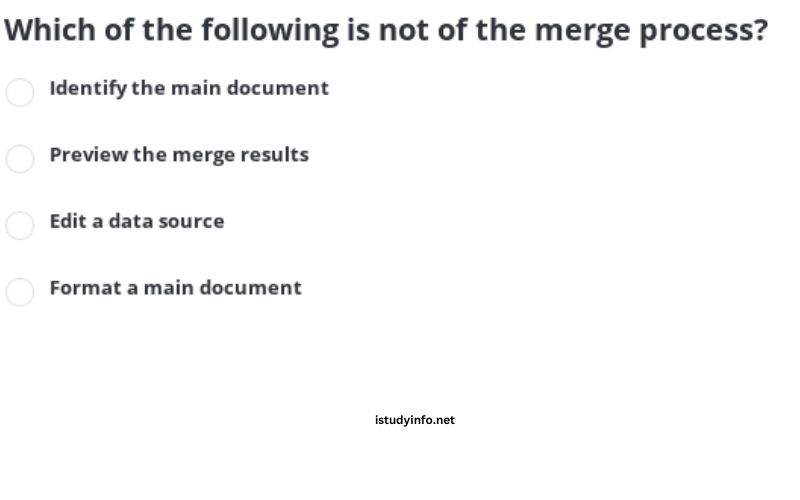
Which of the Following Is Not of the Merge Process
The merge process is a complex and multifaceted undertaking, but it does not include the following:
- Data Extraction: While data extraction is a critical component of the merge process, it is not the merge process itself.
- Data Visualization: Visualizing the merged data is an important step in the data analysis and decision-making process, but it is not part of the merge process.
- Data Governance: Establishing and maintaining data governance policies and procedures is essential for ensuring the quality and integrity of the merged data, but it is not a direct part of the merge process.
Best Practices for a Smooth Merge Process
To ensure a successful and efficient merge process, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Establish Clear Goals and Objectives: Clearly define the purpose and expected outcomes of the merge process to guide the project.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage with key stakeholders, including data owners, IT teams, and business units, to ensure buy-in and alignment.
- Implement Robust Data Governance: Develop and enforce data governance policies to ensure data quality, consistency, and security throughout the merge process.
- Utilize Automation and Technology: Leverage data integration tools and technologies to streamline the merge process and reduce the risk of manual errors.
- Continuously Monitor and Improve: Regularly review the merged dataset, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to the merge process.
To ensure a successful merge process and unlock the full potential of your data, consider working with a data integration expert. They can help you navigate the complexities of data merging, implement best practices, and deliver a unified, high-quality dataset that drives informed decision-making and business growth.
Conclusion
The merge process is a critical component of effective data management and integration, enabling organizations to consolidate information from multiple sources and gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations, customers, and market. By understanding the key steps, common challenges, and best practices associated with the merge process, you can ensure a smooth and successful data integration initiative that delivers valuable insights and supports informed decision-making.